7 Common Food + Science Questions Answered

We eat, we cook, we watch people cook, and through all that, we still may not know how it all happens on a scientific level. At least in a way that we can comprehend. Find out through these food and science facts.
Below are 7 concepts you may have questioned about in your food encounters.
The food + science questions:
- Why does spinach shrink so much when cooked?
- How do cans last so long without preservatives?
- How do beans get canned?
- What is fermentation?
- What is the difference between frying and baking?
- Why does gnocchi float after a while?
- Why are eggs good binders?
1. Why Does Spinach Shrink so Much When Cooked?
We put an abundance of spinach in our pot or pan, yet after some minutes the term “abundance” cannot be used to describe how much spinach there is anymore. More like a tiny amount. Well, why does it shrink so much?
It is important to note that spinach leaves don’t have as much fiber as the stems. This is so the leaves can absorb sunlight easier to produce photosynthesis. Other vegetables have stronger fibrous structures or starch resources that only soften them rather than shrink them so much. So when the spinach is cooked, it releases a lot of water and the cell walls are broken down, making it softer and smaller.
Looking for combinations to make spinach yummy? Check out the Vegan Bowl Guide: Simple & Healthy
2. How do Cans Last so Long Without Preservatives?

Often times the cans we purchase from the store can last years. Yet some other items on the shelves cannot last nearly as long. How do they manage to make the expiration date so far from the present?
Well, bacteria and other microorganisms are responsible for spoiling our food. They feed and therefore produce waste that is not healthy for humans to eat.
In the fridge, the multiplying of bacteria is slowed down and in the freezer even more, which is why food lasts longer in these areas than at room temperature.
Cans, on the other hand, last a very long time without needing these colder temperatures.
Since cans are sealed, no new bacteria or microorganisms can enter. The bacteria that is already in the can is killed by the heating process.
As long as the can isn’t opened, it can last a very long time, but still not forever.
There are a few reasons why they don’t last forever:
- If the can gets wet, bent, or dropped, it could change the perfect seal of the can.
- If it lies in warm temperatures or in sunlight dormant microorganisms in the can could slowly reform.
- If after the heating process there is still some bacteria because the termination of them is not completely guaranteed.
- The flavor of the food inside changes over time.
Perhaps to understand better, read the process of canning below.
Looking for recipes using beans? Check out this Black Bean Burger Salad (gf+vo)
3. How do Beans get Canned?
Simply taking beans, putting them in a can, and closing the can, is NOT the whole process. It is actually insanely more elaborate to ensure bacteria-free beans and long-lasting cans.
This is the process in a nutshell:
- Cleaning: the beans are cleaned and the different colored, unusual sizes, and broken beans are tossed out.
- Hydrating: they are hydrated in water for several hours.
- Note, some companies change the water halfway through and others skip this part.
- Blanching: blanching happens at high temperatures for a short amount of time, sometimes being cooled after.
- Goal: to remove gases and enzymes from the beans to prevent oxidation later on. It also may lessen the number of pathogens (harmful bacteria, viruses, or other microorganisms).
- Brine: the beans are put into aluminum cans with brine.
- What is brine? Brine is water with 1.8%-3% salt and sometimes sugar.
- Sometimes EDTA, which is an acid chemical made out of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen is added as well as calcium chloride, which reduces oxidation.
- Additional: If they are not just plain beans, at this point other things are also added such as sauces and vegetables.
- Thermal processing: in thermal processing, the beans are cooked, the most common method being pressure steamed.
- Goal: to remove other bacteria.
- Beans are non-acidic. Therefore a spore-forming microorganism (a dormant form of bacteria that requires a lot of heat or chemicals to get rid of) is meant to be killed in this step because they can create toxins.
- Cooling: to keep the can intact and prevent thermophilic bacteria the cans are cooled.
- Thermophilic bacteria: bacteria that do well in high temperatures.
4. What is Fermentation?
Fermentation is a metabolic process, aka chemical changes happen. Those come from the microorganisms such as yeast, mold, and bacteria.
The metabolic process occurs when there’s no oxygen and energy is broken down or released from the carbohydrates. Exposure to air could potentially spoil the food. The fermentation produces the chemical Adenosine triphosphate (ATP). There are three types of fermentation: Lactic Acid, Ethanol Alcohol, and Acetic Acid fermentation.
Learn more here.
5. Frying vs Baking
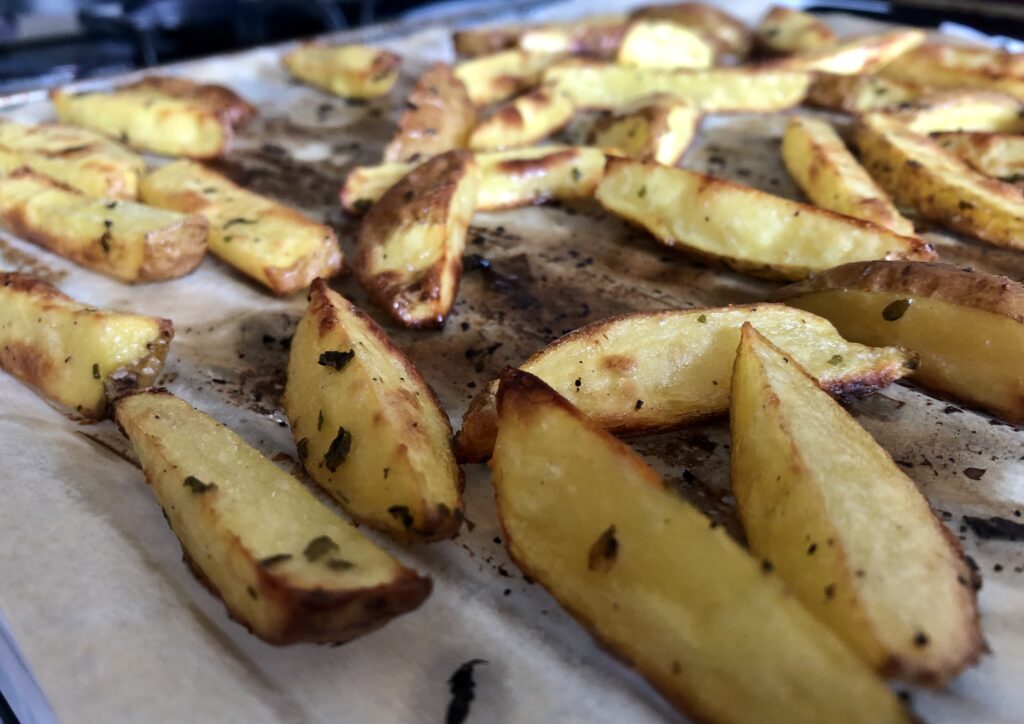

Fries used to be thought of as purely a, well, fried good. Specifically, deep frying. But with health consciousness on the rise, cooking fries by baking potatoes became known.
So if you can make the same food with different methods, what’s the real difference?
Well, when frying, the oil around the food is heated, while in baking it’s just the air surrounding the food that’s heated. Baking also tends to dry out the food more, but the oil surrounding fried food prevents the food from drying out.
Ever wondered why heating the oil before rather than heating the oil with the food inside is important? This is due to the steam preventing the oil from just seeping into the food. Then the oil makes the food crispy. In baking, the process of dehydrating the food results in crispiness.
Another difference is the time the foods cook in these different methods. Baking takes longer because it is transferring air around, while the oil in frying is faster at carrying out energy.
| Frying | Baking |
|---|---|
| The oil around the food is heated | The air surrounding the food is heated |
| The oil prevents the food from drying out | The food dries out more |
| The oil makes fried food crispy | The dehydration results in crispiness |
| The oil in frying is faster at carrying out energy | It takes longer because air is being transferred around |
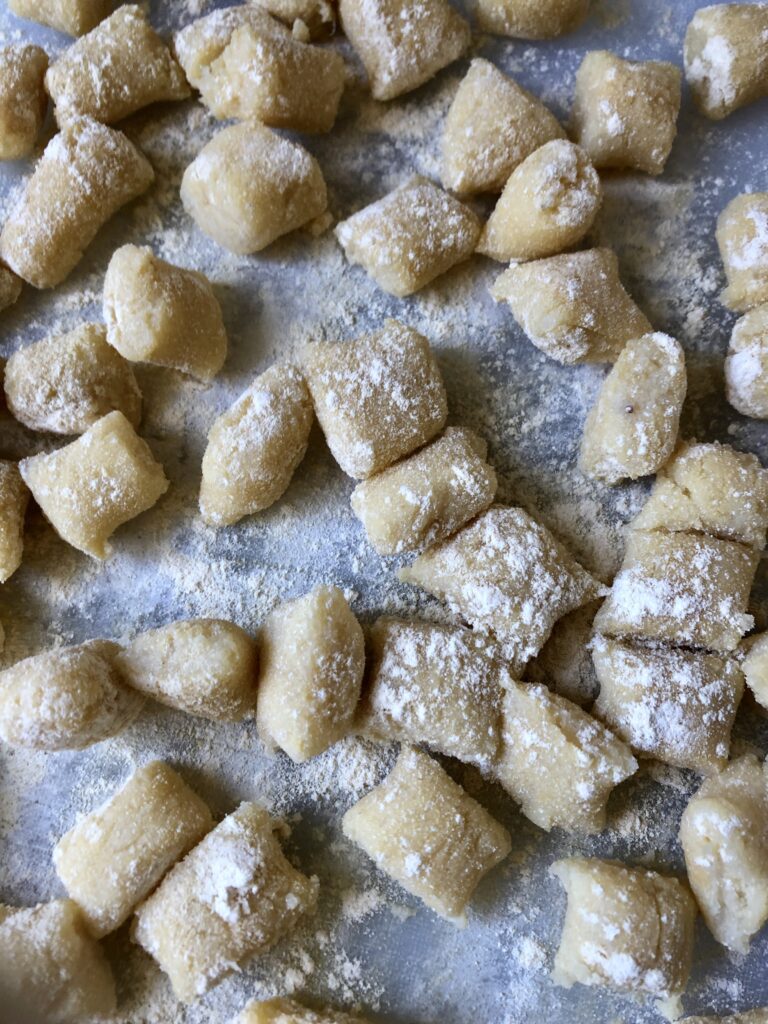

6. Why Does Gnocchi Float After a While?
Right as you put gnocchi in a watered pot, it sinks. This is because at that moment it is heavier than the water.
There is air in the gnocchi though, so as they cook they expand without changing in mass. This lowers the density of gnocchi, making it lighter than the water, so it can eventually float.
As you’ve probably seen recipes always instruct boiling water, that’s because the gnocchi floats up with the air bubbles from the boiling water.
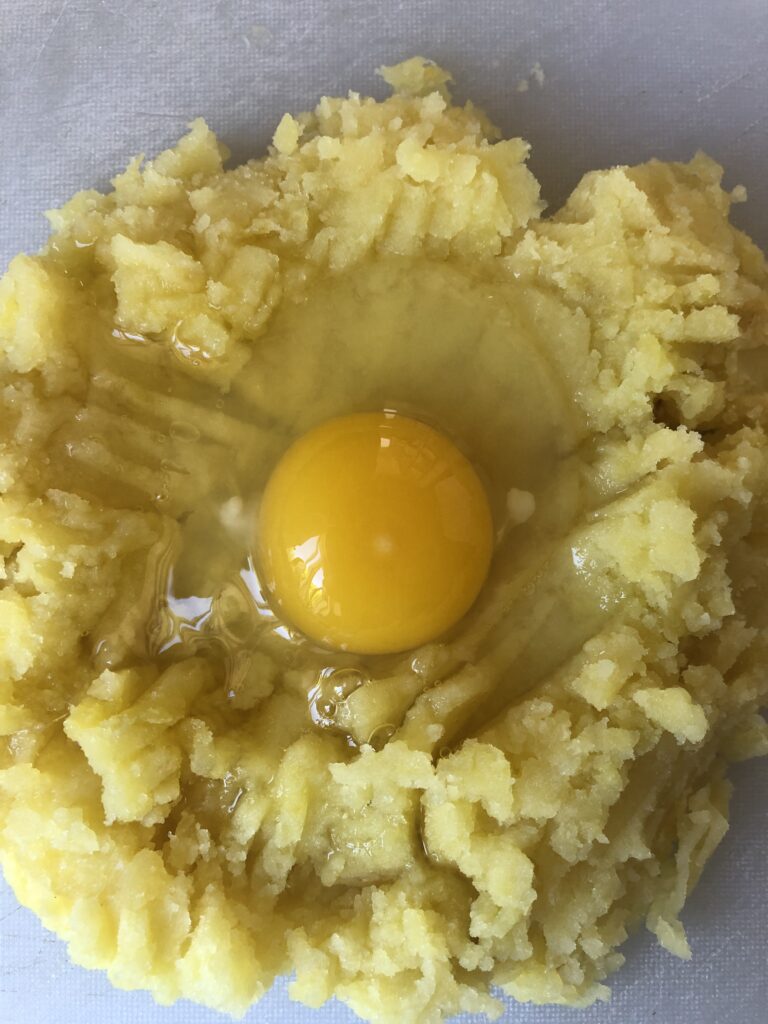

7. Why Are Eggs Good Binders?
You’ve probably realized how common eggs are in baked goods. That’s because eggs are essential binders for many recipes. Why? It’s the proteins in eggs that help bind things together. The yolk, specifically, is an emulsifier that helps bind fats and liquids together. Then when eggs are heated they firm up which helps give structure.



Leave a Reply